Self-sovereign Identity (SSI) and the Triangle of Trust
Trust in everyday life relies on familiarity and understanding - what people know, measure, and perceive as true. But how can entities, such as individuals, organizations, or devices, establish trust without prior knowledge or direct interaction? In the physical world, trust often forms through a Triangle of Trust involving three key roles: issuers, holders, and verifiers.
Understanding the Triangle of Trust
The Triangle of Trust illustrates how different parties establish and verify trust between one another:
- Issuers: Entities that create and issue credentials. These can be governments, organizations, or other trusted authorities.
- Holders: Individuals or entities that receive and hold credentials. They use these credentials to prove their identity or claims.
- Verifiers: Parties that request credentials to confirm the identity or claims of the holder, such as banks, employers, or service providers.
Real-world example: Traveling to another country
When you travel to another country, the Triangle of Trust comes into play:
- Issuers: The government of your destination country issues official travel documents, such as visas or entry stamps, to verify your eligibility for entry.
- Holders: You, the traveler, hold these credentials and present them to the immigration authorities to prove your identity and purpose.
- Verifiers: Immigration officers and border control personnel act as verifiers, checking the validity of your credentials to determine if you meet the entry requirements.
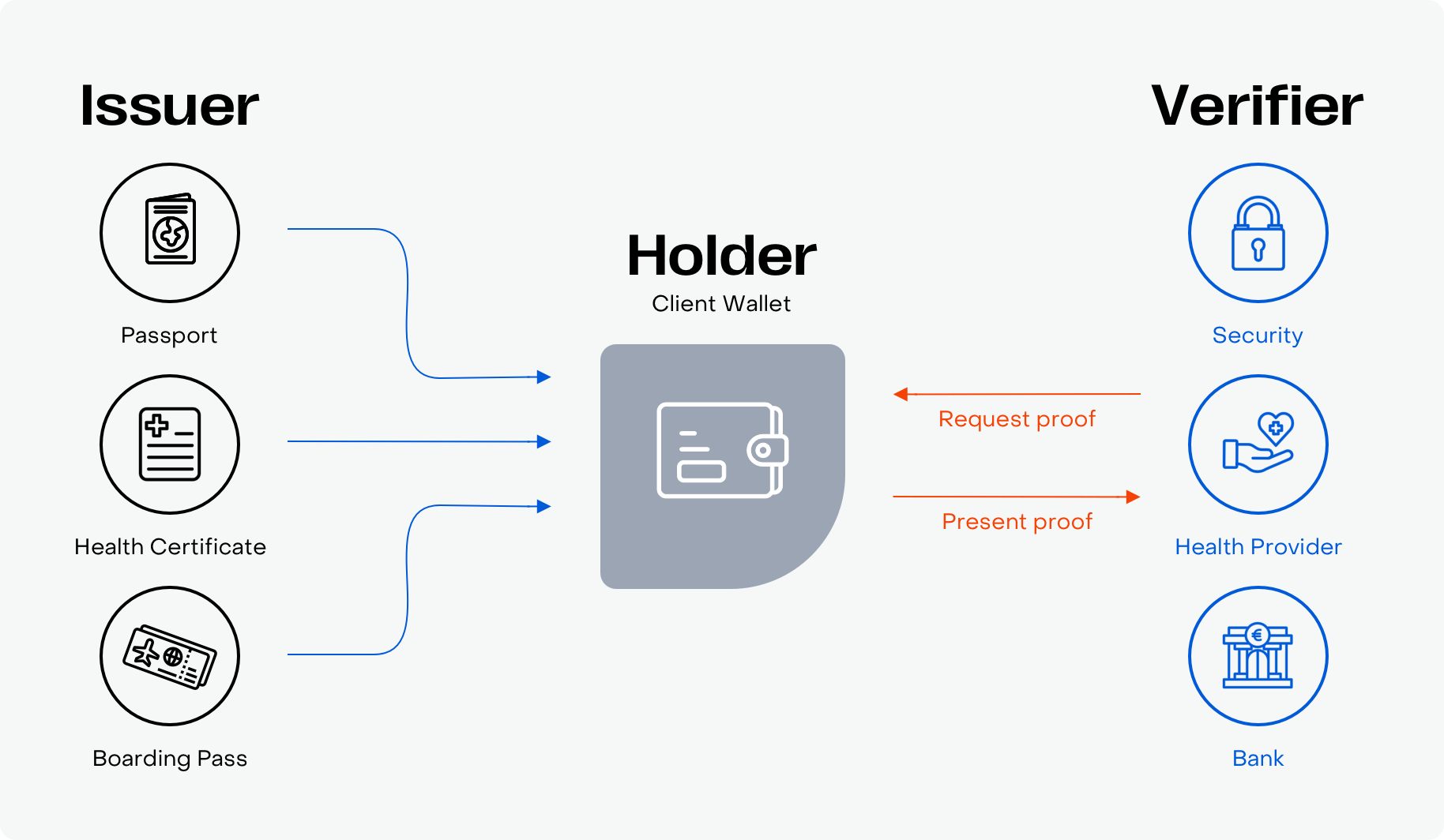
The Triangle of Trust in the digital world
In the digital world, these trust relationships become more complex. For instance, before booking a holiday home, renting a car, or planning a vacation, you must provide official documents to establish trust. This process often requires service providers to handle and protect your information securely, complying with local regulations, which can be both time-consuming and costly.
How SSI simplifies the Triangle of Trust
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) transforms the Triangle of Trust by digitizing and streamlining trust-building processes. Here’s how:
-
Identity assurance
Offers a secure digital identity solution that reduces errors, forgeries, and the risk of document theft.
-
Privacy and security
Empowers you to control your personal data, sharing only what is necessary for verification and reducing the need for companies to store sensitive information.
-
Efficiency and cost effectiveness
Enables instant, remote verification of identity, saving time and resources for both individuals and organizations.
-
Compliance and accessibility
Ensures that data handling complies with privacy regulations and facilitates easy access to necessary documents.
SSI establishes trust more rapidly in digital interactions, enhances privacy, reduces costs, and ensures regulatory compliance.
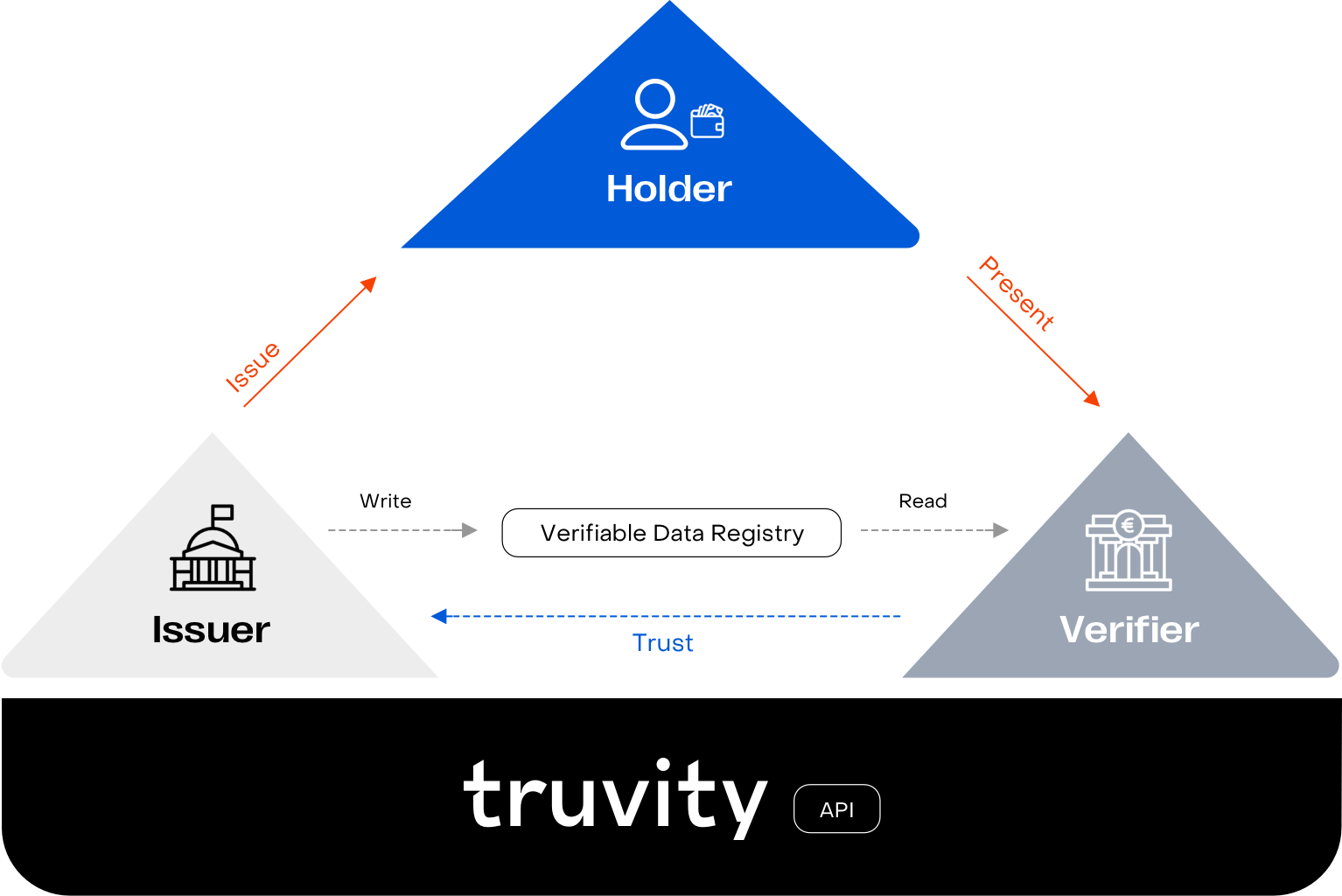
How the Truvity Platform enables the Triangle of Trust
The Truvity Platform applies the principles of SSI through core components such as Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials (VCs). Its APIs and SDKs support seamless integration, enabling the development of trust-based apps for any business.
- For developers: Learn how to integrate Truvity services using the SDKs in the Truvity SDK section.
- For business leaders: Discover how leveraging trust with SSI can enhance customer relationships, improve security, and streamline operations in the Platform overview page.