Verifiable presentations (VPs)
Verifiable presentations (VPs) provide a secure and flexible way to share verifiable credentials (VCs) with a verifier while preserving the integrity and authorship of the data.
What are verifiable presentations?
Verifiable Presentations (VPs) are machine-readable digital containers that package one or more verifiable credentials (VCs). They ensure that the information within is verifiable by cryptographic proofs, allowing the verifier to trust the origin and integrity of the presented data.
According to the W3C Verifiable Credentials Data Model a verifiable presentation is:
A tamper-evident presentation of information encoded in such a way that authorship of the data can be trusted after a process of cryptographic verification. Certain types of verifiable presentations might contain data that is synthesized from, but does not contain, the original verifiable credentials (for example, zero-knowledge proofs).
Key features of verifiable presentations
- Secure sharing: VPs enable secure sharing of credentials between holders and verifiers, ensuring disclosure only of the necessary information.
- Selective disclosure: Holders can choose which parts of their credentials to share, protecting their privacy by revealing only the required information.
- Cryptographic proofs: Applies cryptographic signatures to prove the authenticity and integrity of the presented credentials and confirm they remain not tampered.
- Interoperability: Compatible with various digital identity systems and protocols, enabling seamless interactions across different platforms.
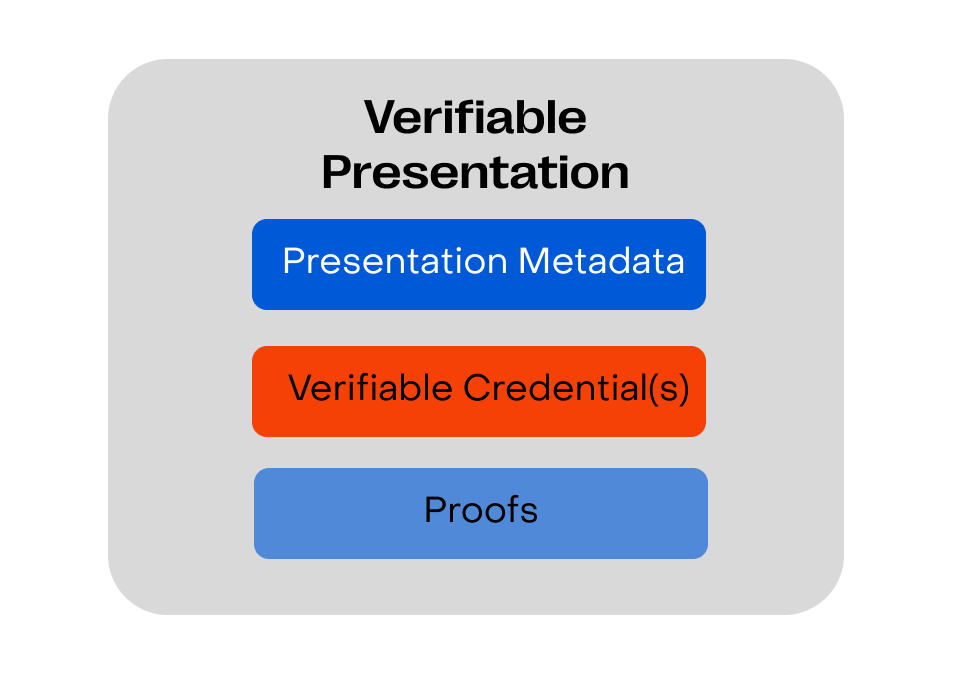
Example of a verifiable presentation structure
Below is a simplified illustration of a Verifiable Presentation's structure:
How verifiable presentations work
-
Credential packaging: The holder selects one or more verifiable credentials (VCs) stored in their digital wallet to include in the presentation.
-
Selective disclosure: The holder decides which specific data or claims within the VCs to disclose, based on the request from a verifier. This allows for minimal exposure of personal information.
-
Proof Creation: The VP is digitally signed by the holder, creating a cryptographic proof that verifies the authorship and integrity of the credentials within the presentation.
-
Presentation to Verifier: The holder submits the VP to the verifier, who uses the cryptographic proofs to validate the authenticity and integrity of data.
Benefits of using verifiable presentations
- Enhanced Privacy: Allows users to share only necessary information, minimizing data exposure and protecting personal privacy.
- Increased Trust: Provides cryptographic evidence of the integrity and authenticity of data, ensuring reliable and trusted digital interactions.
- Flexibility: Supports multiple credentials in a single presentation, making it versatile for various use cases.
- Streamlined Verification: Simplifies the verification process for organizations by providing a standardized and interoperable way to validate credentials.
Further reading
- Understand verifiable credentials and their role in SSI verifiable credentials.
- Learn how to issue a verifiable presentation using Truvity SDK.